Nichols plot
The Nichols plot is a plot used in signal processing and control design [1] [2] [3].
Use in Control Design
Given a transfer function,
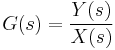
with the closed-loop transfer function defined as,
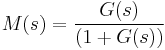
the Nichols plots displays 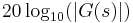 versus
versus 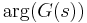 . Loci of constant
. Loci of constant 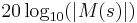 and
and 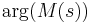 are overlaid to allow the designer to obtain the closed loop transfer function directly from the open loop transfer function. Thus, the frequency
are overlaid to allow the designer to obtain the closed loop transfer function directly from the open loop transfer function. Thus, the frequency 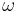 is the parameter along the curve. This plot may be compared to the Bode plot in which the two inter-related graphs -
is the parameter along the curve. This plot may be compared to the Bode plot in which the two inter-related graphs - 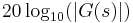 versus
versus 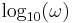 and
and 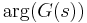 versus
versus 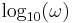 ) - are plotted. Note that the decibel convention shown above,
) - are plotted. Note that the decibel convention shown above, 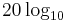 is not unique; another convention sometimes used is
is not unique; another convention sometimes used is 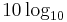 .
.
In feedback control design, the plot is useful for assessing the stability and robustness of a linear system. This application of the Nichols plot is central to the Quantitative feedback theory (QFT) of Horowitz and Sidi, which is a well known method for robust control system design.
See also
References
- ^ Isaac M. Howowitz, Synthesis of Feedback Systems, Academic Press, 1963, Lib Congress 63-12033 p. 194-198
- ^ Boris J. Lurie and Paul J. Enright, Classical Feedback Control, Marcel Dekker, 2000, ISBN 0-8247-0370-7 p. 10
- ^ Allen Stubberud, Ivan Williams, and Joseph DeStefano, Shaums Outline Feedback and Control Systems, McGraw-Hill, 1995, ISBN-10: 0070170525 ch. 17